(a)
(i) Stage the Gibbs-Dalton's law
(ii) For a given mixture by the Gibbs Dalton's Law show that cpm = Σxi c pi
Where cpm = specific heat capacity at constant pressure of the mixture, c pi = specific heat capacity at constant pressure of any constituent I, and. x i = mass fraction of the constituent
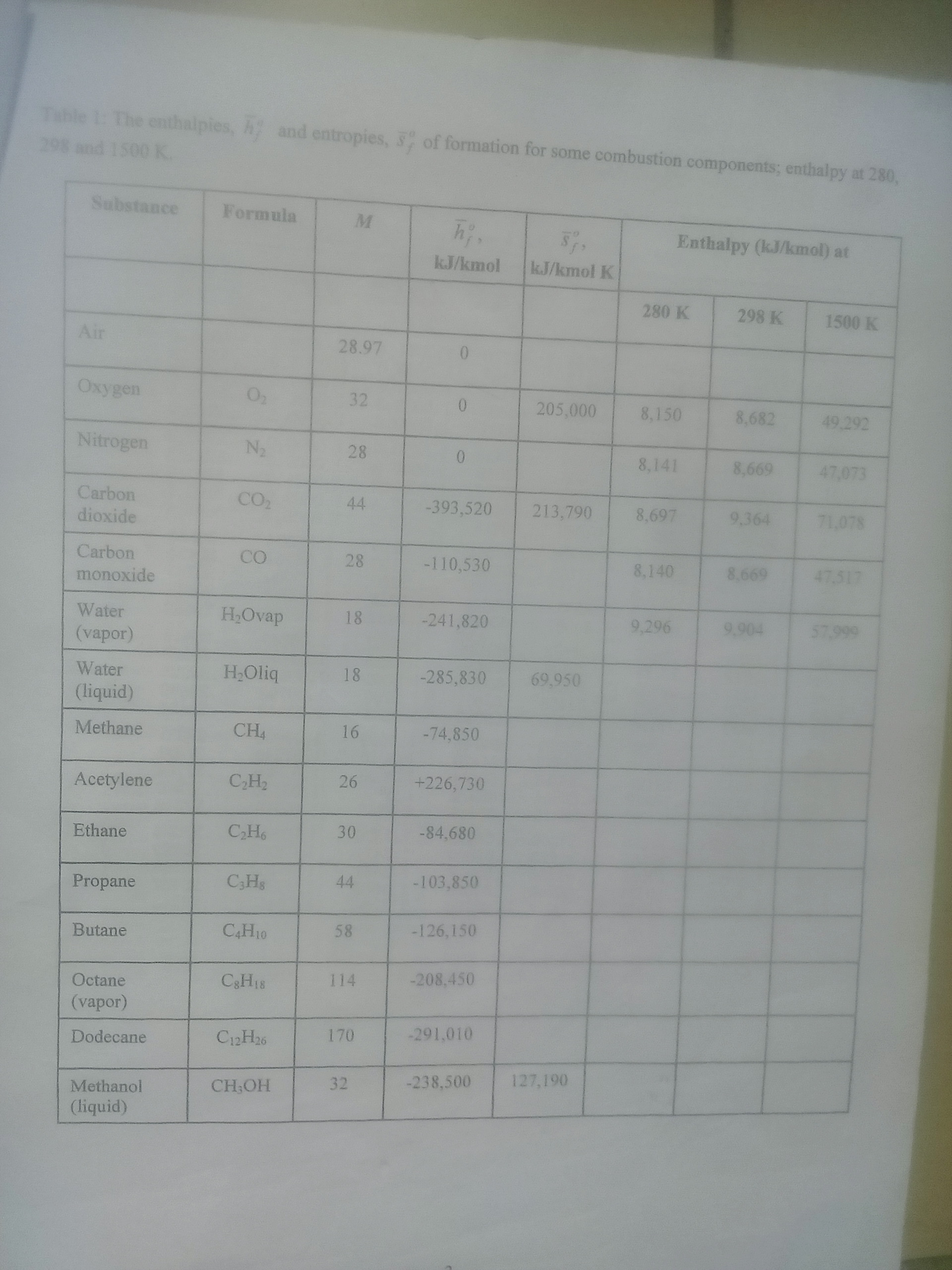
(b) the gas in an engine cylinder has a volumetric analysis of 12% CO2 , 11.5% O2 and 76.5% N2 . The temperature at the beginning of expansion is 1000 0 C and the gas mixture expands reversibly through a volumetric ratio of 7 to 1, according to the law pv1.25 = constant. determine for the mixture.
(i) The specific heat capacity at constant pressure c pm
(ii) The specific gas constant R m
(iii) The specific heat capacity at constant volume c vm
(iv) The work done per unit mass of gas and
(v) The heat flow per unit mass of gas
The values of c p for the constituents averaged over the temperature are as follows c p for CO 2 = 1.271kJ/kgK; c p for O 2 = 1.110kJ/kgK; c p for N 2 = 1.196kJ/kgK;
Question Two
(a) Distinguish between the following
(i) Stagnation and static pressure
(ii) Stagnation and static temperature and
(iii) Stagnation and static enthalpy
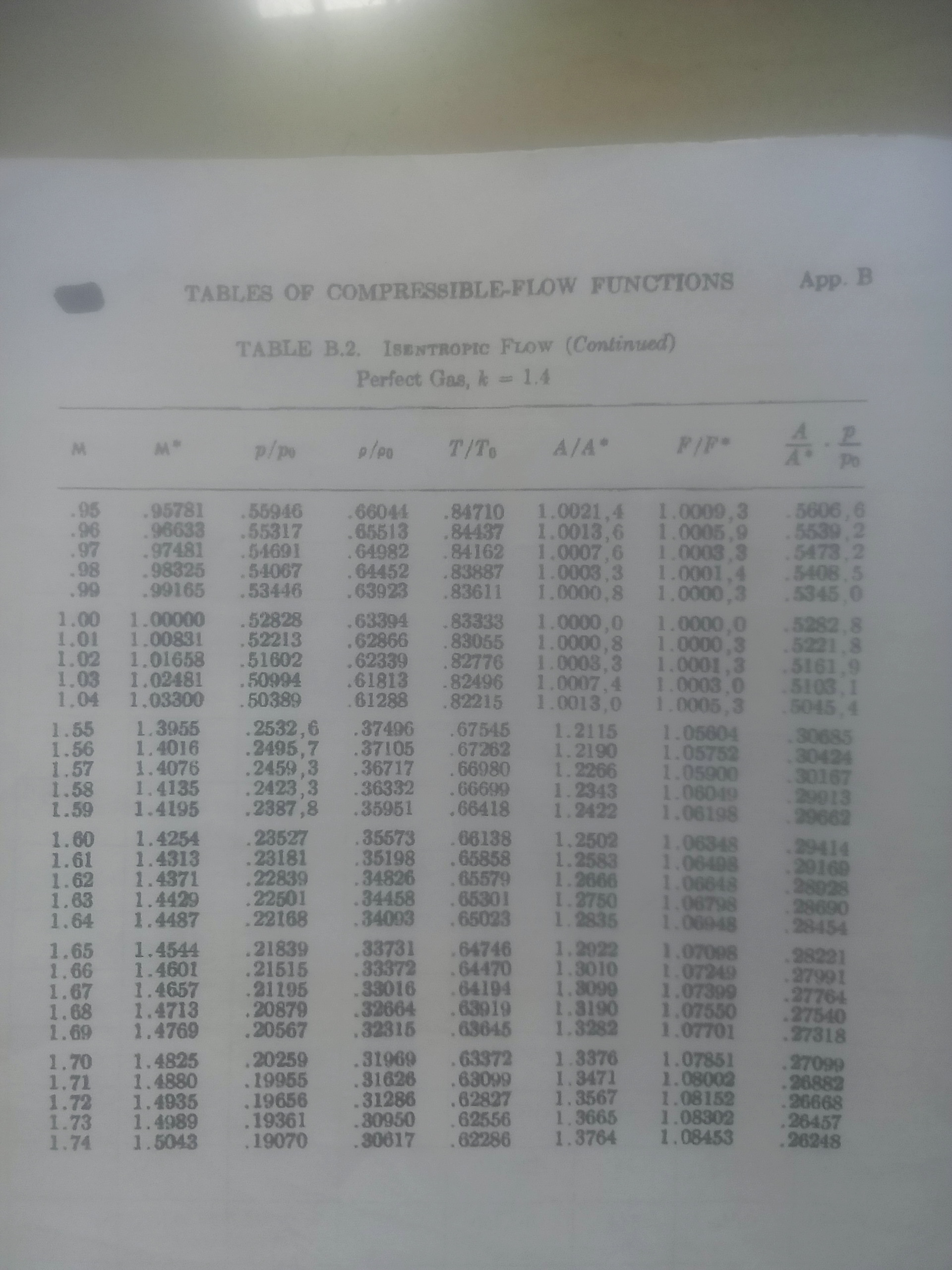
(b) Air flow isentropically from atmosphere at a pressure of 0.5kpa and 15 0 to a 600mm square duct where the Mach number is 1.6. Calculate the static pressure, the velocity and the mass flow rate in the duct. Also determine the pressure and velocity at the point with the minimum cross sectional area
Question Three
(a)
(i) How is the heating value of a fuel related to the enthalpy of combustion of that fuel?
(ii) What are the higher and the lower heating value of a fuel?
(iii) What does the dew point temperature of the product gases represent? How is it determine?
(b) Liquid propane (C3 H 8 ) enter a combustion chamber at 25 0 C at the rate of 0.05kg/min where it is mixed and burned with 50 percent excess ai that entes the combustion chamber at 7 0 C. An analysis of the combustion games reveals that all the hydrogen in the fuel burn to h 2 0 but only 90 percent of the carbon burns to CO 2 , with the remaining 10 percent forming CO. If the exit temperature of the combustion games is 1500K, determine
(i) the mass flow rate of air, and
(ii) the rate of heat transfer from the combustion chamber.
Question Four
(a)
(i) Differentiate between stoichiometric and actual air-fuel ratio
(ii) What is combustion? Highlight three (3) reasons why incomplete combustion occurs
(b) Octane (C 8 H 18 ) burns completely with 120% of theoretical air. Determine
(i) The combustion equation
(ii) The air-fuel ratio on a molar and mass basis
(iii) The mass flow rate of air used to burn fuel at a rate of 1.4kg/min
(iv) The mass of each product of the combustion per unit mass of fuel burned and
(v) The mass fraction of each reactant.
Question Five
(a)
(i) Under what condition does the reversible work equal irreversibility for a process
(ii) How does useful work differ from actual work? For what kind of systems are there two identical
(iii) Consider two systems that are at the same presume as the environment. The first system is in the same temperature as the environment, Whereas the second system is at a lower temperature than the environment. How would you compare the exercise of these these two systems?
(iv) What is the second-law efficiency?How does it differ from the first-law efficiency?
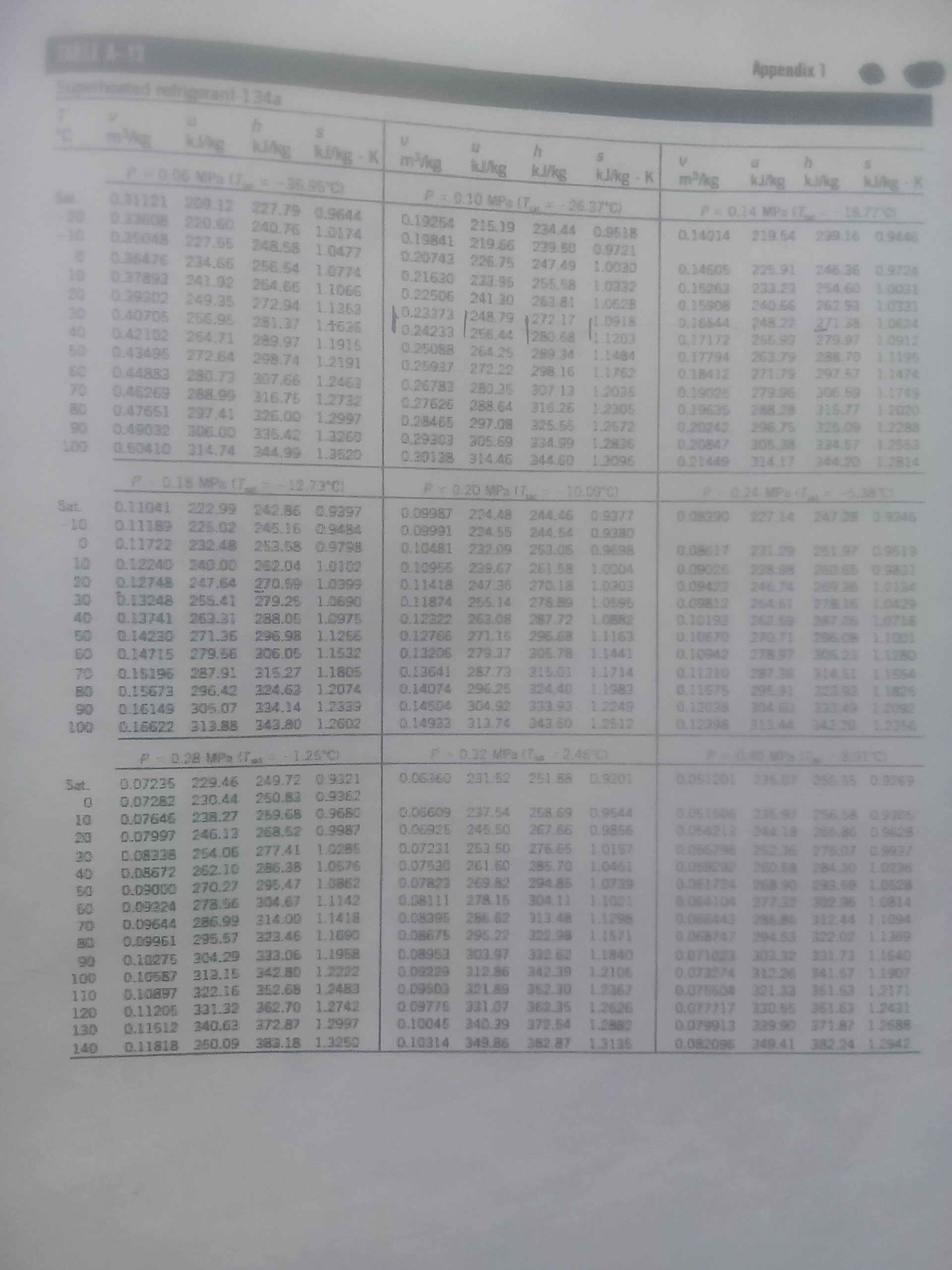
(b)A piston-cylinder device initially contains 1.4kg of refrigerant-134a at 140kPa and 20 0 C. Heat is now transferred to the refrigerant, and the piston, which is resting on a set of stops, starts moving when the pressure inside reaches 180kPa. Heat transfer continues until the temperature reaches 120 0 C. Assuming the surroundings to be at 25 0 C and 100 kPa, determine:
(i) the work done;
(ii) the heat transfer;
(iii) the exergy destroyed; and
(iv) the second-law efficiency of this process
question six
(a)
(i) List four (4) major advantages and disadvantages each of fuel cells compared to other power conversation devices.
(ii) Discuss two potential applications of fuel cells where their unique attributes make them attractive.
(b)
(i) Explain the significance of Gibbs free energy, G. State the maximum efficiency of fuel cell in terms of Gibbs free energy and enthalpy. How is the work done in a fuel cell related to the Gibbs free energy?
(ii) A direct methanol fuel cell uses methanol as fuel instead of hydrogen. Calculate the enthalpy and entropy for the methanol combustion reaction :
CH3 OH(liq) + 3/2 O2 ----> CO2 + 2H2 O(liq)